What is Portuguese man o' war or Oceanic Physalia?

The Portuguese man o' war (Physalia physalis), Physalia (Physalia physalis) is a colony of hydroid polyps that is mistakenly associated with the jellyfish family. The beautiful "jellyfish" is often found in the Canary Islands. It looks very beautiful, the color is simply amazing, but, as you know in nature, the brighter and more beautiful the color, the more dangerous its owner.
The Portuguese man o' war lives in the cooler waters of the Atlantic Ocean, especially it can often be found on the resort beaches of the Canary archipelago (Tenerife, Fuerteventura). It is worth noting that it also enters the Mediterranean Sea through the Strait of Gibraltar due to strong currents from the Atlantic Ocean, but, as a rule, after strong storms.
However, recently more and more physalia can be seen on the beaches of Malaga. And on the beaches of Alicante, Valencia, Benidorm is extremely rare.
What do we have to do upon contact with the Portuguese man o' war and what not to do?
 The first step is to treat the area with vinegar, then remove the stuck pieces of tentacles. This must be done carefully, without pressing hard and without scraping the skin, because you will crush the adhering jellyfish cnidia (tentacle particles). Recommend bite solution, best white vinegar (3–5%), apple cider vinegar or malt vinegar (barley) is fine. By the way, there are already ready-made solutions based on vinegar.
The first step is to treat the area with vinegar, then remove the stuck pieces of tentacles. This must be done carefully, without pressing hard and without scraping the skin, because you will crush the adhering jellyfish cnidia (tentacle particles). Recommend bite solution, best white vinegar (3–5%), apple cider vinegar or malt vinegar (barley) is fine. By the way, there are already ready-made solutions based on vinegar.
Important! The vinegar solution is used with this type of "jellyfish" (Physalia utriculus y P. physalis), and not with other jellyfish. For example, in the Mediterranean there is a type of jellyfish la Pelagia Noctiluca and in contact with it, do not use acetic solutions.
Remember! A big mistake is treating the area with fresh water or ice. First, fresh water affects the remaining stinging cells on the skin, which burst and release the neurotoxin. And secondly, with fresh water, the poison penetrates the skin better. Ice treatment, which also consists of fresh water, will only worsen the condition and increase pain later.
If you want to cool the affected area of the skin, put ice in a plastic bag. But even here I will say that, on the one hand, the condensate will consist of fresh water, and on the other hand, there is evidence that cooling worsens the forecast. Hence the conclusion, neither hot nor cold water will also help, so use medium temperature water.
Do not use alcohol solutions, nor ammonia solutions, or soda will also worsen the condition after 24 hours. AT There are many myths and legends in the world, I will immediately say that the healing "properties of urine" in this situation will also greatly worsen the clinical picture. So neither soap, nor shaving cream, nor lemon juice, nor dishwashing detergent, nor cola can be used to treat a skin area in contact with a Portuguese boat.
First aid is the application of a cream with lidocaine and corticoids, an antihistamine.
How toxic is this Pacific man o' war or bluebottle?
 Contact with it can cause severe pain, breathing problems, and even cardiac arrest. The neurotoxin secreted by its tentacles is highly toxic. The very body of the Portuguese boat is a blue gelatinous bubble that is not poisonous to humans, but tentacles are dangerous. The thing is that they are long, are under water, grow up to 14 meters in length and carry millions of stinging cells that contain neurotoxin.
Contact with it can cause severe pain, breathing problems, and even cardiac arrest. The neurotoxin secreted by its tentacles is highly toxic. The very body of the Portuguese boat is a blue gelatinous bubble that is not poisonous to humans, but tentacles are dangerous. The thing is that they are long, are under water, grow up to 14 meters in length and carry millions of stinging cells that contain neurotoxin.
Under safety protocols in Spain, a ban on swimming in the sea is created for a Portuguese man-of-war if this organism has been seen more than twice. If you swim in the ocean in the Canary Islands, ride jet skis, jump into the ocean water from a yacht, then it will be very useful for you to know a few very important recommendations upon contact with this instance.
It is not surprising that this rather beautiful ocean dweller can arouse great interest, especially from children. However, in its attractive lilac color lies the danger and poisonous toxin. Contact with the tentacles causes severe burning and redness of the skin. Therefore, approaching and direct contact with tourists will have serious consequences.
What does a skin burn look like when in contact with pby the Portuguese man o' war?
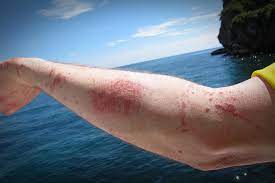 The clinical picture highlights erosive skin lesions with a linear arrangement. Affected area of the body upon contact with tentacles of a portuguese man-of-war mainly causes a local lesion in the area of contact and pain, which can be very severe. The toxin causes inflammation and swelling immediately upon contact, with a progressive appearance of papules, vesicles, blisters, and possible flaking. There may be a feeling of numbness, weakness, cramps, muscle pain, tachycardia, sweating.
The clinical picture highlights erosive skin lesions with a linear arrangement. Affected area of the body upon contact with tentacles of a portuguese man-of-war mainly causes a local lesion in the area of contact and pain, which can be very severe. The toxin causes inflammation and swelling immediately upon contact, with a progressive appearance of papules, vesicles, blisters, and possible flaking. There may be a feeling of numbness, weakness, cramps, muscle pain, tachycardia, sweating.
Burning of the affected area of the skin is accompanied by the appearance of red spots on the skin, and if the burn is very extensive. I note that the appearance of pigmented scars and keloids (disproportionate growth of scar tissue) is very common, but local necrosis and infection of the wound is practically impossible (this is not a snake bite, for example). All of these listed complications usually do not occur after the bite of a simple jellyfish. Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and headache are also common.
Medical assistance to improve the condition in the first 24 hours after contact withby the Portuguese man o' war
IN SPAIN YOU CAN BUY THESE DRUGS:
Pain relief cream with lidocaine:
- Dermovasigil
- Emla (recommended)
- Anesteal
- Lambdalina
- Titanorein lidocaina
- Versatis
- Xilonibsa Aerosol
- Xylonor
Cream with corticoids for external use:
- Beclometasona (Menaderm)
- Betametasona (Allergic)
- Clobetasol (Clovate, Decloban)
- Clobetasona topico (Emovate)
- Diflorasona
- Diflucortolone
- Fluticasona topico (Cutivate, Fluticrem)
- Mometasona (Elocom, Elocom plus) - recommended
Antihistamines:
- Bilastina (Bilaxten, Ibis)
- Desloratadina (Aerius) - recommended
- Ebastina (Ebastel)
- Loratadina
- Rupatadina
If the affected area was treated correctly in a timely manner and there is no inflammation or infection, then there is no need to use antibiotics, for example, Cloxacillin.
To summarize, patients should be aware that dermatological skin lesions after contact with physalia may be present for up to several months. Itching and burning of the skin may sometimes appear on contact with salt water. To restore the skin, it is recommended to use rosehip oil or any other cream that contains rosehip.
(scientific article testing chemical solutions for steractyl cells of the Portuguese man-of-war)
Thanks to the author of the article for the interesting information about the Portuguese man-of-war, or Oceanian Physalia. It is a colony of hydroid polyps and is found in the cool waters of the Atlantic Ocean.
Based on this material, it became completely clear what should be done when contacting the Portuguese man-of-war and what should not be done.
and before they washed it with fresh water and it always got worse
Thanks to the author of the article for the interesting information about the Portuguese man-of-war or ocean Physalia. From the article, I learned that the Portuguese man-of-war is actually a colony of hydroid polyps, and not a jellyfish, as many people mistakenly believe. It lives in the cold waters of the Atlantic Ocean, but can sometimes enter the Mediterranean Sea. It was also mentioned that recently Physalia can be found more often on the beaches of Malaga.
I thank the author of the article for useful information about the Portuguese man-of-war or ocean Physalia. The material is a description of this creature, its habitat and the dangers associated with it.
Thank you for the article. We met this miracle on the beach of Cuba. The burn is minor and there are no major symptoms. But it's unpleasant.