If you want to have your body diagnosed or are looking for a specific examination in clinics and hospitals in Valencia, then in this section we offer all the basic medical examinations. First of all, you need to make an appointment and get a doctor's referral. After which you will be recommended a laboratory or medical institution where you can quickly perform the analysis you need, or other diagnostics of the body you need.
Our patients are served in the clinics and hospitals of Valencia on an accelerated basis if you have a private medical insurance policy. If you are a private patient, you will be admitted without waiting in line.
How much does a medical examination cost in Valencia? We provide pricing information for private patients only. Patients with insurance policies always receive authorization from their insurance company and pay nothing extra.
Also use our resource to determine the cost of the most popular procedures and surgeries. If the list does not contain the name you need, contact us via the feedback form, and we will provide the necessary information.
Diagnostics, examinations, tests, check-ups in Valencia
VALINTERMED specializes in organizing comprehensive and specialized medical examinations in Valencia. We offer programs "Check Up" and cardiac screenings for athletes. In addition, we provide consulting services, complete information about treatment, help clients choose the best place to stay during treatment, and also translate all necessary documents.
Diagnostics of the body in Valencia is an important part of the medical services provided, offering patients access to advanced methods of examination and assessment of health. In Valencia, a city with a highly developed medical infrastructure, diagnostics are carried out using modern equipment and innovative technologies. This makes it possible to accurately identify various diseases in the early stages and develop effective treatment plans.
Patients can benefit from a wide range of diagnostic procedures, including laboratory tests, MRI, CT, ultrasound, as well as other specialized tests. These services are provided as part of a holistic approach to health, which provides an accurate and comprehensive understanding of each patient's physical condition. Thus, diagnosis in Valencia is a key step towards effective treatment and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Checkup (check up). Body examination packages
VALINTERMED cooperates with the main diagnostic centers that carry out "check-up" examinations in Valencia (Spain).
Diagnostics of oncological diseases
Screening programs designed for all age categories, taking into account individual genetic predisposition.
If you are the owner of a private insurance policy (we recommend SANITAS) and you are interested in any of the programs listed here, then you must first make an appointment with Dr. Korzhikov.
After consultation with a specialist and an orderly medical history of the patient, you will be given all the necessary directions. Because some test referrals issued require authorization from your insurance company. For example, MRI or CT, as well as Colonoscopy and Gastroscopy.
Note that many patients go for a consultation with a doctor already with ready-made analyzes that do not need to be translated and repeated. This means that many patients want a second examination or a second expert opinion. In this case, we do not request repeat tests unless absolutely necessary.
Private patients without insurance policies who want to undergo "CHECAP in VALENCIA" will be required to first make an appointment with Dr. Korzhikov. They do not need any authorizations, they will be accepted out of turn and informed in detail about prices and discounts.
Medical examinations in Valencia with descriptions
| Type of analysis/test | Description, purpose |
|---|---|
| Amniocentesis | Analysis of fluid obtained with a needle that is inserted through the abdominal wall to detect possible abnormalities in the fetus |
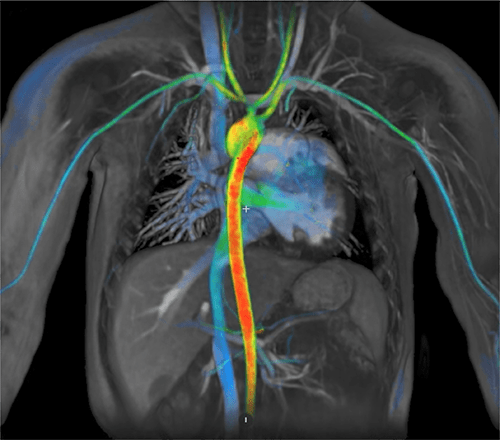
| Arteriography (angiography) | X-ray using a radiopaque dye that is injected through a thin tube (catheter) inserted through the artery of interest to locate and indicate or highlight an obstruction or defect in the artery |
| Audiometry | Assessment of the ability to hear and distinguish sounds in certain tones and volumes using headphones |
| Auscultation | Standard examination with a stethoscope of the chest to detect abnormal heart sounds |
| X-ray with barium contrast (barite porridge) | X-ray examination to look for ulcers, tumors, or other abnormalities |
| Biopsy | Extraction and examination of a tissue sample under a microscope to look for cancer or other abnormalities |
| Blood pressure measurement | Test for high blood pressure (hypertension) or low blood pressure (hypotension), usually with inflatable cuffs wrapped around the arm |
| Blood test | Measurement of parameters of substances in the blood to assess the function of organs. Diagnosis and control of various body disorders |
| Bone marrow aspiration | Extraction of a bone marrow sample with a needle for examination under a microscope. Identification of disorders in hematopoietic cells |
| Bronchoscopy | Direct visual inspection with an optical probe to detect a tumor or other abnormality of the bronchi and lungs |
| Cardiac catheterization | Examination of the function of the heart and its structure using a catheter that is inserted through an artery to the heart |
| Chorionic biopsy | Sample extraction for examination and determination of the presence of abnormalities in the fetus |
| Chromosome analysis | Microscopic examination to detect a genetic disorder or to determine the sex of the fetus |
| Colonoscopy | Direct visual inspection with an optical probe to detect a tumor or other abnormality |
| Colposcopy | Direct examination of the cervix with a magnifying lens |
| Computed tomography (CT) | Computed radiographic examination to detect structural abnormalities |
| Cone biopsy | Removing and taking a sample of tissue for examination, usually using a hot wire loop or laser |
| Sowing | Cultivation and examination of microorganisms to detect infection caused by bacteria or fungi |
| Dilation and curettage (curettage) of the cervix and uterus | Examination of a sample under a microscope to detect abnormalities in the lining of the uterus. Using a small instrument (curettes). |
| Bone densitometry (DEXA) | Low dose radiographic examination to determine bone thickness |
| Cardiac echocardiography | Study of the structure and function of the heart using ultrasound |
| Electrocardiography (ECG) | Study of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes attached to the arms, legs and chest |
| Electroencephalography (EEG) | Studying the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes |
| Electromyography (EMG) | Recording the electrical activity of muscle tissue. Small needles are used that are inserted into the muscle |
| Electrophysiological heart test | Test for deviation in rhythm or electrical conduction using a catheter. Inserted into a blood vessel and led to the heart |
| Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) | Radiographic examination of the biliary tract, made after injection of a radiopaque dye and using a flexible tube |
| Endoscopy | Direct visual examination of the internal structures of the upper gastrointestinal tract using a flexible viewing tube |
| Enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) | Tests that involve mixing blood samples with substances that can cause allergies (allergens) or with microorganisms to check for specific antibodies |
| Fluoroscopy | A continuous x-ray examination that allows the doctor to see the inside of a functioning organ. Dynamic research. |
| Hysteroscopy | Direct visual inspection of the inside of the uterus |
| Intravenous urography | Radiographic examination of the kidneys and urinary tract after intravenous injection of radiopaque dye |
| Arthrocentesis (joint puncture) | Extraction and examination of fluid from the space inside the joints to check for the presence of blood cells, crystals formed from minerals and microorganisms |
| Laparoscopy of the abdominal cavity | Direct visual inspection using an optical probe inserted through an incision in the abdomen to diagnose or treat abnormalities in the indicated area |
| Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) | An imaging diagnostic test that uses a strong magnetic field to detect structural abnormalities |
| Mammography | Radiological examination to screen for or detect breast cancer |
| Thoracoscopy | Direct visual examination of the area of the chest between the lungs using an optical probe inserted through a small incision just below the sternum |
| Myelography of the spinal cord | Plain or computerized X-ray of the spine after radiopaque injection |
| Nerve conduction study | Test to determine the speed of transmission of a nerve impulse using electrodes or needles inserted along the path of the nerve |
| Occult Blood Test | Test to detect blood in stool. Colon |
| Ophthalmoscopy | Direct visual inspection using a hand-held instrument that illuminates the inside of the eye to detect retinal abnormalities |
| Pap smear/Pap test | Microscopic analysis of cells collected from the cervix to detect cancer |
| Abdominal Paracentesis | Extraction of fluid from the abdominal cavity for its analysis |
| Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography | Radiographic examination of the liver and biliary tract after injection of a radiopaque dye into the liver |
| Positron emission tomography (PET) | Diagnostic imaging test using particles that emit radiation (positrons) to detect functional abnormalities |
| Pulmonary function tests | Measurements of the lung's ability to hold air, move and exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide) while a person is in a special chamber |
| Gammagraphy | Diagnostic imaging test using particles that release radiation (radionuclides) to detect abnormalities in the structures or functions of organs |
| Reflex analysis | To determine nerve conduction |
| Retrograde urography | Radiological examination of the bladder and ureters after the introduction of radiopaque dye into the ureter |
| Sigmoidoscopy | Direct visual inspection through an optical probe to detect tumors or other abnormalities in the far colon |
| Allergy tests, prick test | Allergy tests, done by placing a solution containing a possible allergen on the skin and then applying light pressure to the skin with a needle |
| Spinal puncture / lumbar puncture | Taking cerebrospinal fluid using a needle that is inserted into the lumbar region to detect violations of this fluid |
| Spirometry of the lungs | Pulmonary function test |
| Stress Test / Cardiac Ergometry | Checking heart function during exercise using a treadmill and electrocardiogram (if this person is unable to exercise, a substance is used to mimic the effects of exercise) |
| Pleural fluid puncture / Thoracocentesis | Removal or withdrawal of fluid from the pleural space with a needle to detect abnormalities |
| Thoracoscopic lung examination | Visual inspection of the surfaces of the lungs, pleura and pleural space using an optical probe |
| Tympanometry / impedancemetry | Measuring middle ear pressure resistance (impedance) with an instrument inserted into the ear to determine the cause of hearing loss |
| Ultrasonography / ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | Imaging using sound waves to detect structural or functional abnormalities |
| Analysis of urine | Chemical analysis of a urine sample to detect proteins, sugar, ketones, and blood cells. Microscopic analysis |
| Venography | X-ray examination using a radiopaque dye (similar to arteriography) to detect diseases of the venous system |